Ovarian apoplexy is one of the gynecological diseases that cause the appearance of a clinical picture of an acute abdomen. This dangerous pathology in the absence of timely medical care can lead to very serious complications. However, the occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen is not a rare symptom. Almost all women from time to time experience pain in this area associated with certain phases of the menstrual cycle. But ovarian apoplexy is exactly the disease in which it is worth paying attention to pain and seeking qualified medical help as early as possible. Knowing the symptoms of ovarian apoplexy helps to diagnose this pathology in a timely manner.
Methods of diagnosis and symptoms of ovarian apoplexy
The main clinical symptom of ovarian apoplexy, as well as other gynecological diseases that cause the clinical picture of an acute abdomen, is sudden pain in the lower abdomen. The occurrence of pain in this case is explained by irritation of the receptor field of the ovarian tissue, the effect of the outflowing blood on the peritoneum, and also by spasm in the basin of the ovarian artery. In addition to the pain syndrome with apoplexy, a woman is worried about weakness, nausea and vomiting, dizziness and fainting. But depending on the form of pathology, the clinical picture of ovarian apoplexy may differ somewhat.
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy:
- symptoms of ovarian apoplexy in painful form;
- symptoms of ovarian apoplexy in hemorrhagic form;
- Basic methods for diagnosing ovarian apoplexy.
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy in painful form
Painful form of ovarian apoplexy is observed when a hemorrhage occurs directly into the tissue of the follicle or corpus luteum. There is no bleeding into the abdominal cavity. With this form of the disease, the main symptom of ovarian apoplexy is pain in the lower abdomen, which does not radiate, and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. There are no signs of bleeding into the abdominal cavity. When examining the patient, the color of the skin and mucous membranes remains normal, the pulse and blood pressure do not change. Palpation marked pain in the iliac region on the right. On gynecological examination, the uterus is of normal size, the affected ovary may be slightly enlarged and painful on palpation.
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy in hemorrhagic form
The mild hemorrhagic form of rupture of ovarian tissues clinically very much resembles the pain form, but in moderate and severe forms, the symptoms of ovarian apoplexy are somewhat different, since they are associated with intra-abdominal bleeding. The pain syndrome occurs acutely, often appears during physical exertion or sexual intercourse, radiates to the rectum, leg, lower back and external genitalia. The patient is also concerned about weakness, dizziness, nausea and vomiting. The patient's skin and mucous membranes are pale, and cold clammy sweat may occur. Blood pressure is reduced, tachycardia occurs, which is explained by blood loss. On palpation, a sharp pain in the iliac region is determined, with a bimanual gynecological examination, a painful, somewhat enlarged ovary is palpated on the side of the apoplexy.
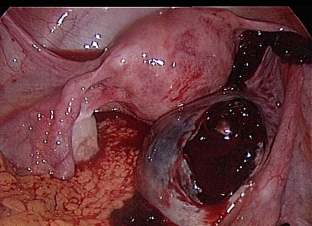
Basic methods for diagnosing ovarian apoplexy
The following laboratory and instrumental research methods are used to diagnose ovarian apoplexy:
- complete blood count: moderate leukocytosis in pain form, decrease in hemoglobin level, leukocytosis in hemorrhagic form;
- ultrasound examination: a small amount of hypoechoic fluid with a fine suspension in the Douglas space in case of pain, a significant amount of fine and medium-dispersed fluid in the abdominal cavity, with irregularly shaped hyperechoic structures in hemorrhagic form of ovarian apoplexy;
- laparoscopic examination: ovulation stigma is observed - a small spot raised above the surface of the ovary with signs of bleeding, in the form of a cyst of the corpus luteum or the corpus luteum itself with a rupture or defect.






Add a comment