Vaginal candidiasis usually affects women of childbearing age and causes a lot of trouble. On the one hand, this disease is characterized by itching, burning, unpleasant discharge and pain during intercourse, and on the other hand, when it enters the chronic stage, it can provoke a number of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. A significant role in the prevention of vaginal candidiasis is played by the strengthening of the body's defenses, since it is the weakening of the immune system that most often causes the activation of this infectious agent.
Reasons for developing vaginal candidiasis
The causative agent of vaginal candidiasis is called yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, belonging to the conditionally pathogenic human flora. Under normal conditions, these microorganisms live on the skin and mucous membranes of various organs - the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and external genital organs. Different strains of candida fungus have different degrees of pathogenicity, and in representatives of different races and geographic regions - for example, among residents of African countries or the Mediterranean - one or another causative agent of vaginal candidiasis may be active. However, their activity is influenced by nutritional habits, living conditions, and the specifics of microbiocenosis in different regions of the world.
Candida fungus quickly dies when boiled and treated with antiseptic agents, but easily adapts and multiplies in conditions of fluctuations in temperature and acidity of the habitat. Often, vaginal candidiasis occurs as an asymptomatic carriage and is activated when the body's defenses are weakened. The reasons for the development of vaginal candidiasis can be:
- hormonal imbalance (for example, during pregnancy);
- diseases associated with immunosuppression (HIV, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis);
- taking certain medications (antibiotics, cytostatics, corticosteroids, hormonal contraceptives);
- exacerbation of allergic diseases;
- endocrine disorders.
Most often, Candida fungus develops in the conditions of the vaginal mucosa. But it happens that candida persist in the intestine and from there colonize the vaginal flora. Usually, Candida fungus affects only the surface layer of the mucous membrane, but under certain conditions it can spread to deep tissues, and even to adjacent organs. There is evidence of the likelihood of sexual transmission of vaginal candidiasis, as well as the possible infection of the infant when passing through the birth canal in a sick woman.
How to recognize vaginal candidiasis in a patient
Usually, candidiasis is asymptomatic, and in the acute phase, a woman comes to the appointment with the main complaint of copious vaginal discharge, whitish, cheesy and with an unpleasant odor. In addition, patients are concerned about vaginal itching, burning sensation and pain during intercourse. Itching worse after exercise, after washing, during menstruation.
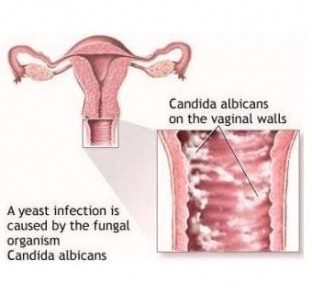 On examination, there is an edematous, hyperemic vaginal mucosa with a curdled coating. Foci of inflammation of different sizes, an eroded surface with scalloped edges of spots is visible under the whitish films.
On examination, there is an edematous, hyperemic vaginal mucosa with a curdled coating. Foci of inflammation of different sizes, an eroded surface with scalloped edges of spots is visible under the whitish films.
Basic principles of treatment of vaginal candidiasis
The complex of treatment of vaginal candidiasis should consist of three important steps: this is the effect on the fungus itself, the treatment of the disease that provoked its development, and the treatment of all concomitant pathologies.
With a mild course, you can get by with the use of local remedies, if the disease has become chronic, systemic drugs are prescribed and the treatment is repeated in courses. Polyene antibiotics, antimycotic preparations are used, in addition, anti-inflammatory and disinfectants are prescribed. If, according to the study, vaginal candidiasis is polymicrobial in nature, combine antimycotic drugs with metronidazole.
To prevent recurrence of the disease, patients are advised to be careful about taking various medications, strengthen immunity and not neglect regular visits to the gynecologist.






Add a comment