Treatment of patients with surgical infection of soft tissues has always been a complex problem, which has not lost its relevance even today. The incidence of wound infection in the developed world reaches 1-2% among patients who seek surgical care.
In about ⅓ of these patients, purulent-septic complications of the tissues of the lower extremities are noted, caused by the main pathology: diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, metabolic disorders, systemic diseases of the connective tissue.
Read our article on estet-portal.com for the most up-to-date information on the use of sorbents for purulent complications in surgery.
Factors of development of purulent complications in surgery
A surgical wound and the phases occurring in it constitute a complex cascade of general biological reactions of the body in response to a focus of tissue destruction and microbial contamination. The course of this cascade is influenced by a number of factors: the age of the patient, nutritional habits, body weight, the presence of secondary infection of the wound, the state of blood circulation in the lesion and the body as a whole, disturbances in the water and electrolyte balance, immune status, chronic concomitant diseases, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Follow us on Instagram!
In many cases, the course of the wound process in surgery during operations on soft tissues is aggravated by the influence of the underlying disease, concomitant pathologies and dysfunctions, intoxications, cachexia, multiple organ failure and diseases of internal organs. Under such conditions, the possibilities of carrying out specific surgical treatment of the wound are significantly limited. Therefore, there is a growing need to improve the effectiveness of local treatment, in order to avoid the occurrence of foci of destruction and purulent inflammation.
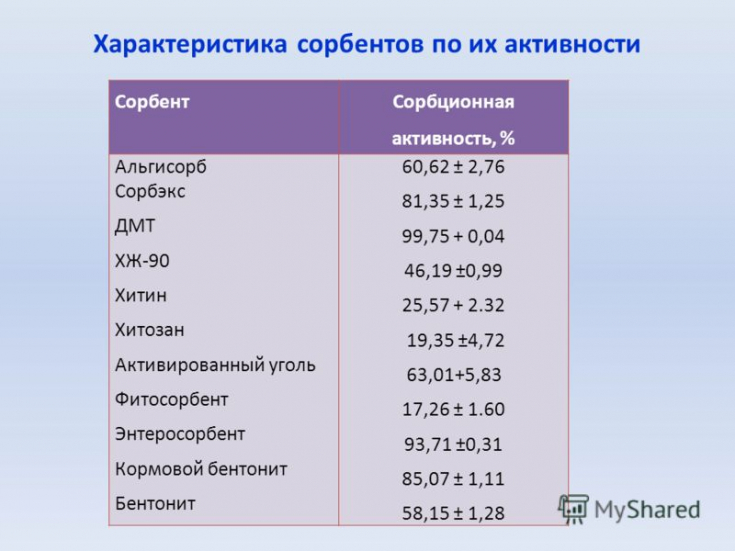
The place of sorbents in purulent surgery
Among the drugs used for local treatment of purulent wounds, hydrogel films, hydrocolloids, foam, alginates, hydrofibers and sorbents are common. Their use in surgery is determined by the stage of the wound process (purulent-necrotic phase, phases of granulation and epithelialization), and the components themselves and the dressing material made on their basis should ensure the absorption of pathological secretions from the wound (necrobiosis products and necrotic tissues, microorganisms and their toxins). ) and the optimal microclimate in the wound (humidity, air access and temperature conditions), isolate the wound from additional contamination by microorganisms from the external environment. The bandage, when removed, should not cause pain or discomfort to the patient.
One of the main factors in surgery that affects rapid healing is maintaining a moist environment and pH in the wound.
In this sense, hydrocoloid dressings are more effective for the healing of chronic non-infected wounds, while dressings with the addition of alginates and sorbents have shown high efficiency in the treatment of purulent wounds in surgery, especially when it is necessary to ensure the removal of necrotic tissue detritus.
Autodermoplasty technique with perforated graft
The use of sorbents capable of retaining sorbed substances from the wound at the liquid / solid phase interface, and suitable for the reverse process of desorption of pre-loaded drugs, makes it possible to effectively control the healing process of a purulent wound in surgery.
Electrical dressing: treatment of infected wounds
Physical properties of sorbents
Such sorbents are used in the form of powder, granules, fibers, tissues impregnated with a sorbent, which affect the wound process not only due to the sorption of toxic substances, but also by catalytic oxidation and blockade of electrochemical processes in the bacterial wall.
In addition to the ability to retain toxic discharge from the wound on its surface, sorbents maintain normal osmotic pressure and prevent the destruction of surrounding tissues. The above processes are typical for the first phase of the wound process in surgery and are the most important period in the treatment, since they form the conditions for the restoration of reparation processes and prevent the development of complications.
What antiseptics should be used in the treatment of burn wounds
Effective innovative sorbents
Methoxane (polymethylsiloxane) − organosilicon sorbent with a developed porous structure (pores 18-100 nm in size) ? is able to adsorb (take away from the wound) exudate and desorb (give into the wound) substances immobilized in the pores, with which it was previously saturated. The immobilized substance is contained on the surface or in the pores of the sorbent matrix and creates a prolongation effect, maintaining a high local concentration of drugs in the wound.
Rehabilitation after rhinoplasty: drugs, procedures, tips

At the same time, local detoxification is carried out due to further adsorption and immobilization of toxic substances and metabolites contained in tissue fluids. A significant advantage of the sorbent is its ability to maintain the therapeutic concentration of the antibiotic in the wound for a long time (up to 8 days) by desorption (release) of biologically active substances (antibiotics and enzymes) immobilized in its pores.
The sorbent causes a significant local detoxification effect due to sorption and a 50% reduction in the amount of discharge from the wound.
The manifestations of local inflammation are reduced, there is a decongestant effect. Cleansing of the wound and the transition of the degenerative-inflammatory process into a reparative one accelerates by an average of 3-5 days.
The use of sorbents in surgery in the treatment of purulent wound process accelerates the healing process, helps to reduce the severity of inflammation, accelerates the cleansing of wounds from necrotic tissues and the development of granulations.
Fat transplantation for facial rejuvenation







Add a comment