Oily skin and enlarged pores – one of the most frequent complaints with which patients turn to a dermatologist. To solve this problem, local (natural or synthetic retinoids) or systemic (oral contraceptives, spironolactone, isotretinoin, laser and photodynamic therapy) treatment is prescribed.
The most effective of the above therapeutic methods is the use of isotretinoin, which is associated with a high risk of side effects (dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes and skin, which in severe cases can cause skin infections).
Intradermal botulinum toxin injections are reported to be promising treatments for oily skin without the risk of serious complications.
Peculiarities of the sebaceous glands: causes of oily skin
Sebum contains various fatty acids, wax esters, triglycerides, cholesterol and squalene. Sebum performs an important physiological function – moisturizes and lubricates the stratum corneum of the epidermis, acts as a waterproof barrier, protects the skin from friction, transports antioxidants into the skin, promotes wound healing and has an antimicrobial effect. However, excess sebum production can make the skin prone to acne.
Follow us on Instagram!
Increased oiliness of the skin, increasing throughout the day – typical patient complaint. An overproduction of sebum can be the result of several factors, such as:
• hormonal disorders;
• wet climate.
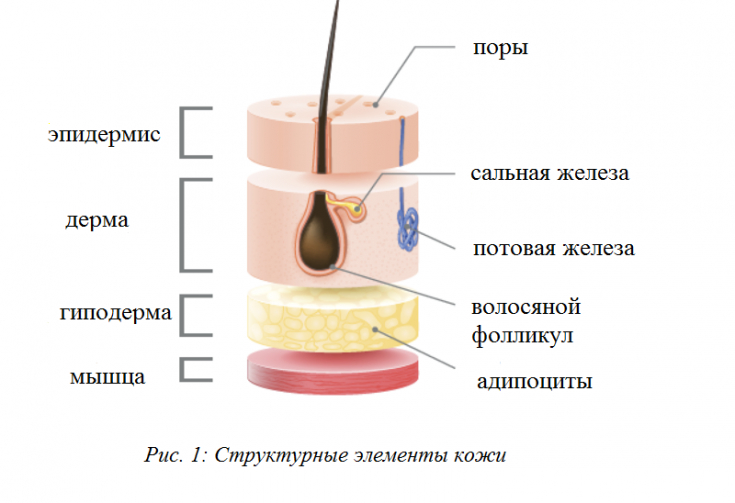
The sebaceous glands are located in the middle layers of the dermis. The greatest density of the sebaceous glands on the face, upper chest, back and scalp, the smallest – on the feet and palms.
Sebum hyperproduction and high density of sebaceous glands, especially in the T-zone of the face (300-900/cm2), can lead to oily skin.
Increased oiliness of the skin: causes and methods of cosmetic effects
The activity of sebum production depends in part on hormones, in particular androgens. The number of sebaceous glands throughout life remains unchanged, but their size, as well as the intensity of sebum production, increases during adolescence. Sebaceous secretion decreases during perimenopause in women and at 60-70 years in men.
Intradermal injections of botulinum toxin for the treatment of oily skin
Botulinum toxin – a powerful neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. Botulinum toxin blocks the transmission of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to the synaptic cleft, preventing it from binding to the postsynaptic membrane and allowing for further muscle relaxation. This helps to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The exact mechanism of action of intradermal injections of botulinum toxin in reducing sebum production is not fully understood, but it is assumed that the substance acts on acetylcholine receptors in sebocytes.
The exact mechanism of action of intradermal injections of botulinum toxin in reducing sebum production is not fully understood, but it is assumed that the substance acts on acetylcholine receptors in sebocytes. The highest density of acetylcholine receptors is observed in the infundibulum of the pilosebaceous complex.
Research on the use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of oily skin
1. Earlier retrospective study (by – Shah), 2008 Participants – 20 patients. Botulinum toxin type A was injected intradermally into the T-zone of the face. After 1 month, 17 of 20 patients noted a significant reduction in pore size and sebum production. The results were confirmed photographically. No complications were recorded.
Cleaning pores for oily skin - decontamination options
2. In Vitro Study (Authors – Li et al), 2013. 20 volunteers took part in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, split-face study in which a reduction in sebum production on the side of the face was observed after injections of botulinum toxin. The authors suggested that botulinum toxin reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands by blocking acetylcholine receptors in the pilosebaceous complex.
3. A prospective study of the effectiveness of intradermal injections of botulinum toxin for excessive sebum production in the forehead (authors – Rose and Goldberg), 2013. The study involved 20 women and 10 men. Using a 30-gauge needle, 3-5 units of abobotulinum toxin A (Dysport) were injected intradermally at 10 points located horizontally in the upper third of the forehead. During the follow-up of a group of patients at 1, 4, 8 and 12 weeks, an objective assessment of the results was carried out by means of photo and sebumetry.
Results: Significant reduction in sebum production in all participants during all return visits (p<0.001). Sebumetry demonstrated a 75% reduction in sebum production at 1 week, 80% at 4 weeks, 73% at 8 weeks, and 59% at 12 weeks post-treatment. Pore size decreased, all patients were satisfied with the results.
4. Prospective, randomized, double-blind study of sebum control by injection of botulinum toxin A into the frontalis muscle (authors – Min et al), 2015. Participants – 42 women divided into 2 groups: the first group was injected with 2 units of the drug at each point (total 10 units), the second group – 4 units of the drug (total 20 units). Botulinum toxin A (& laquo; Botox) was injected intramuscularly into the forehead area (5 points). Patients were re-examined 2, 4, 8 and 16 weeks after the procedure.
Facial cleansers for oily skin
Photos and sebumetry were used to evaluate the results. There was a significant reduction in sebum production within a radius of 0.5 cm from each injection site. An increase in the dosage of the drug did not affect the degree of reduction in sebum production. The authors noted that after injection into the muscle, the toxin can penetrate into the dermal layer, suppressing acetylcholine signals in the pilosebaceous complex. Therefore, direct intradermal injections of botulinum toxin may be more effective in addressing the problem of oily skin than intramuscular injections.
Features of the technique of intradermal injection of botulinum toxin
The target structure in the treatment of oily skin with botulinum toxin injections is the pilosebaceous complex located in the dermis. Too superficial introduction of the product will not provide the desired effect.
A study by Rose and Goldberg documented a case of loss of frontalis muscle tone. Therefore, the optimal injection technique is extremely important both for the effectiveness of therapy and for reducing the risk of intramuscular injection of botulinum toxin.
Some authors suggest injecting the drug at a 75 degree angle to allow intradermal administration without paralyzing the muscle. This approach is especially appropriate when working with the perioral and zygomatic areas. Rose and Goldberg also note that the correct injection of botulinum toxin can be confirmed by extruding the product from the surrounding pores.
The authors of the studies do not describe any serious complications associated with the treatment of oily skin with intradermal injections of botulinum toxin. However, in a study by Rose and Goldberg, there was a case of loss of frontalis muscle tone. Therefore, the optimal injection technique is extremely important both for the effectiveness of therapy and for reducing the risk of intramuscular injection of botulinum toxin.
Adapted from Aesthetics







Add a comment