– a complex process that requires diagnostic instrumental and laboratory studies, a correct assessment of their results and a decision on the choice of therapy. Hyperplastic processes, including polyposis, can be treated conservatively or radically – through surgery.
On estet-portal.com read
how to draw up a therapeutic scheme correctly,as well as what methods of conservative and radical therapy are priority. Conservative treatment of endometrial polyp
Conservative therapy is indicated in combination with surgical treatment, or it is prescribed for young patients with small solitary polyps, without severe breakthrough bleeding and extensive inflammation.
If glandular-fibrous and glandular polypous growths of the endometrium are diagnosed, then hormonal treatment is prescribed, aimed at regulating the hormonal background and stabilizing the menstrual cycle. The duration of hormone therapy lasts from 3 to 6 months.
Most commonly written:• girls and women under 35: estrogen-progestin combined oral contraceptives;
• patients after 35 years of age are shown gestagens;
• women who do not plan to become pregnant within the next 5 years are prescribed the use of an intrauterine system.
Antibiotics – another group of drugs of choice in the treatment of an endometrial polyp, because the cause of the pathology is often hidden in chronic inflammatory processes localized in the pelvic organs and genitals.In the treatment of an endometrial polyp, the therapeutic regimen includes vitamin preparations and dietary supplements. After uterine bleeding, for the timely recovery of the body, the patient is prescribed B vitamins and iron.
Basic methods of diagnosis and treatment of cervical polyp
Surgical treatment of the endometrial polyp: the main types of operations
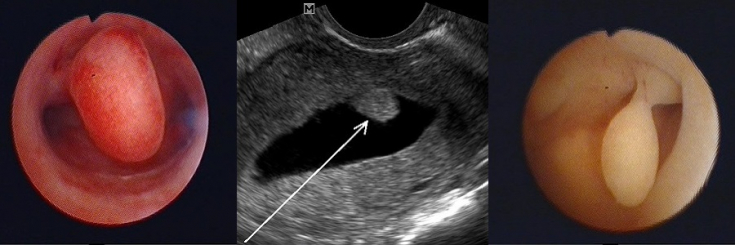
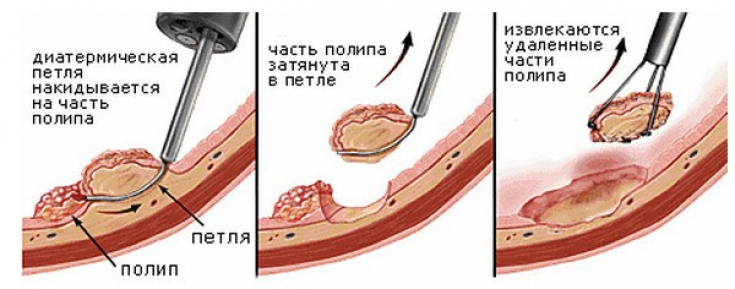
Confirmed diagnosis of endometrial polyp – a direct indication for the appointment of diagnostic hysteroscopy and histological analysis of the obtained tissues. We list the main types of surgical interventions used in the treatment of an endometrial polyp:1. Polypectomy.
Carried out in the presence of a large single pedunculated polyp. Then it is "twisted", and the remaining wound surface is cauterized with electric current or liquid nitrogen. These manipulations prevent, although not always, the formation of new pathological formations. The operation is quick, however, it is performed under general anesthesia.2. Hysteroscopy
– removal of a polyp using an endoscopic hysteroscope, which is inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity.3. Curettage.
New modern methods of treating the endometrial polyp are rapidly replacing this type of therapy.4. Surgery to remove the uterus.
Hysterectomy is extremely rare, and most often when there are signs of malignancy.Read the latest articles in
TelegramPeculiarities of treatment of adenomatous polyps
Adenomatous polyp requires special control, as there is a high risk of its transition from a benign to a malignant form. With such a diagnosis, all women of menopausal age are shown extirpation (removal) of the uterus.
 If there is a serious risk of cancer (burdened heredity, serious hormonal disorders, work in hazardous industries), then the appendages are removed along with the uterus. For patients of childbearing age, only the polyp is removed, but then they are actively monitored.
If there is a serious risk of cancer (burdened heredity, serious hormonal disorders, work in hazardous industries), then the appendages are removed along with the uterus. For patients of childbearing age, only the polyp is removed, but then they are actively monitored.
On the third day after the operation to remove the polyp, a follow-up ultrasound is prescribed.
If the patient has had a hysterectomy, it is important to ensure that the patient:
• Adequate pain relief. The presence of severe postoperative pain sharply worsens the woman's condition and slows down the recovery process;
• proper nutrition to normalize bowel function and prevent constipation and bloating;
• Sufficient and regular physical activity.
After polyp removal, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection.
The sutures are treated daily with a disinfectant solution, working only with sterile instruments. Dressings are done daily, monitoring the condition of the postoperative scar. If necessary, symptomatic treatment is prescribed taking into account chronic pathologies and complaints of the patient.
 The late postoperative period begins in the second week after extirpation and often lasts up to two years. The operation causes a sharp failure of the hormonal background, therefore, drug correction is indispensable.
The late postoperative period begins in the second week after extirpation and often lasts up to two years. The operation causes a sharp failure of the hormonal background, therefore, drug correction is indispensable.
Read also:
Female infertility: types, causes and factors





