The occurrence of the clinical picture of an acute abdomen is a situation that is one of the most dangerous and undesirable in gynecology. An acute abdomen implies the occurrence of a serious and extremely dangerous pathological process in the internal reproductive organs of a woman, which, in order to avoid serious complications, must be eliminated as soon as possible. Torsion of the peduncle of an ovarian tumor is one of the conditions leading to symptoms of an acute abdomen. This pathology provokes the development of necrotic and inflammatory processes in the small pelvis, which can lead to death in a matter of hours. Timely diagnosis and effective treatment of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor helps to avoid such consequences.
Methods for the diagnosis and treatment of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor is one of those gynecological pathologies that cause the appearance of a clinical picture of an acute abdomen. As you know, the concept of "acute abdomen" is common not only in gynecological practice, but also in abdominal surgery. The leading symptom of an acute abdomen is the occurrence of abdominal pain, the exact location of which often cannot be indicated even by the patient herself. In this case, the pain must be urgently stopped and its cause eliminated as soon as possible. Therefore, the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of various diseases in acute abdomen syndrome is extremely important for the correct diagnosis and effective treatment of the pathology that provoked this condition.
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor:
- methods for diagnosing torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor;
- differential diagnosis of torsion of the ovarian tumor stem;
- methods of treatment of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor.
Methods for diagnosing torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor
Diagnosis of torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian tumor is based on the history and general examination of the patient, as well as on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- history data: the patient indicates that she has a previously diagnosed ovarian neoplasm;
- objective examination data: pale skin, cold sweat, rapid pulse, elevated body temperature. The abdomen is swollen, sharply painful at the site of the projection of the neoplasm, muscular defence is observed, positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation;
- general blood test: leukocytosis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- gynecological examination: palpable volumetric formation in the area of the uterine appendages, tight-elastic consistency, painful on palpation. The uterus and appendages on the other side are unchanged;
- ultrasound examination: a volumetric formation in the area of the uterine appendages with signs of a tumor or ovarian cyst is visualized;
- laparoscopy: a cyanotic formation is determined in the small pelvis, which is an ovary with torsion of the leg, a serous or serous-hemorrhagic effusion can be visualized.
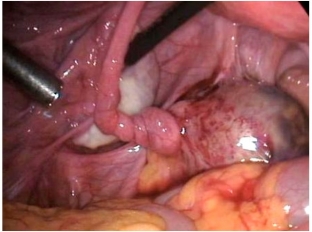
Differential diagnosis of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor
Differential diagnosis is an extremely important step in the diagnostic process of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor. The clinical picture of an acute abdomen, which occurs when the pedicle of an ovarian tumor is twisted, quite often accompanies some other gynecological and surgical pathologies. Most often, torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor has to be diagnosed with acute appendicitis and renal colic. In acute appendicitis, similar symptoms occur, while a gynecological examination will not reveal any changes in the uterine appendages. With renal colic, the nature and localization of pain sensations are somewhat different, the indicators of a general urine test change significantly. Additional research methods, such as plain radiography, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space,
Methods of treatment of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumorTorsion of the peduncle of an ovarian tumor is treated exclusively by surgery. The patient is shown urgent hospitalization and surgical intervention. Currently, laparoscopic and laparotomy approaches are used. Directly during the examination of the pelvic organs, their condition is assessed: if there are no visual signs of neoplasm tissue necrosis, the tumor leg is untwisted and blood circulation is restored. If the type of neoplasm allows, and there are no signs of ischemia and venous stasis, they are limited to resection of the ovary, which allows you to save the reproductive organ. Otherwise, the necessary volume of surgical intervention is the removal of the uterine appendages.








Add a comment