Skin barrier dysfunctions accompanied by dry skin are extremely common symptoms in clinical medicine.
This phenomenon has been called "xerosis".
Xerosis occurs in people of all ages with a frequency of up to 20-40%.
However, most often xerosis occurs in children, especially of an early age. Therefore, the determination of the factors causing the occurrence of skin xerosis, and the development of therapeutic measures for this condition is an urgent problem.
For more information about the features of the structure of the skin and the causes of skin xerosis in children, read the article on estet-portal.com.
- Features of the structure of the skin that cause the occurrence of xerosis in children
- The role of filaggrin protein in the development of xerosis in children Features of the structure of the skin that cause the occurrence of xerosis in children The epidermis of infants is thinner than that of adults and is composed of smaller corneocytes and keratinocytes. As a consequence of − great transepidermal water loss
Follow us on
Instagram!
The stratum corneum of the epidermis of newborns contains 13-15% water.However, the ability to retain this moisture is not perfect, so fluid is quickly lost, causing skin dryness (xerosis). Fluid retention provides intercellular space that fills the gaps between corneocytes of the stratum corneum.
This space includes:
cholesterol;
ceramides; fatty acids.
The lower rows of the stratum corneum, held together by
- lipidic structures
- , form a dense zone that is an obstacle to transepidermal fluid loss and penetration of allergens, toxins and microorganisms into the skin.
- Research on the causes and age-related characteristics of the development of allergic dermatitis
Ceramides
are an important component of the skin barrier and have pronouncedantimicrobial properties. In their composition, ceramides contain a special type of glycerin
− sphingosine, which is involved in the regulation of desquamation rates and affects the functions of keratinocytes.The enzyme sphingomyelinase is a necessary condition for the conversion of sphingolipids into mature ceramides, and its deficiency, which is typical for young children, leads to a rapid impairment of the function of the epidermal barrier
when exposed to adverse factors and, as a consequence, we observethe development of xerosis in children, as well as signs of hypersensitivity
.According to the results of scientific research, with dry skin, there is an imbalance
− a decrease in long-chain fatty acids and ceramides, together with an increase in unsaturated free fatty acids.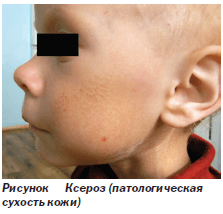
Modern view of epidermolysis bullosa
The granular layer of the epidermisCauses, risk factors and prevention of diaper dermatitis
On the other hand, the basal layer of the skin of
children is well developed, but due toinsufficient production of melanocortin in the first months of life, and sometimes during the first year of life, Melanocytes are less functional and produce relatively little melanin, resulting in fairer skin and greater
susceptibility to UV rays. The role of filaggrin protein in the development of xerosis in children
The cells of the granular layer contain
keratohyalin granules, which include
filaggrin protein
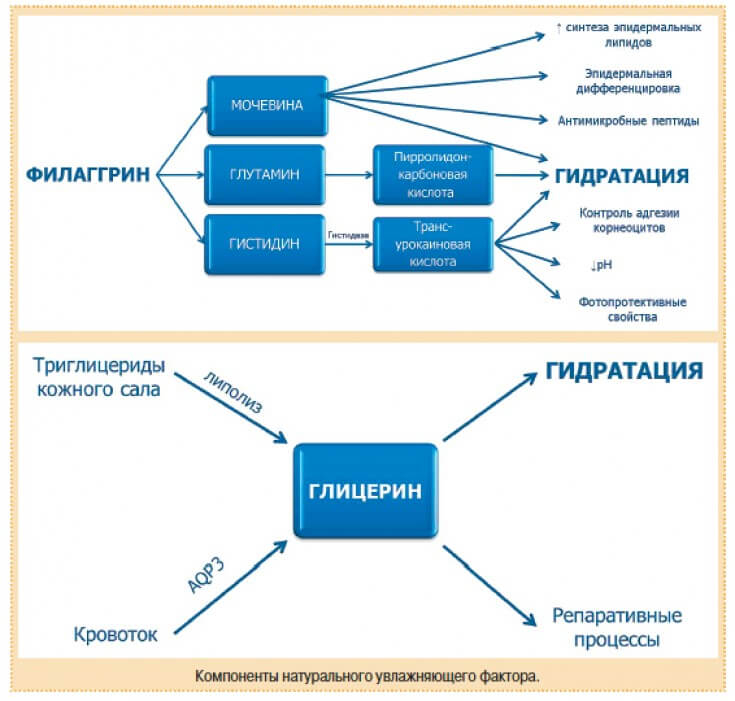 Filaggrin is involved in the formation of the so-called
Filaggrin is involved in the formation of the so-called
These water-soluble compounds are capable of retaining water. Thanks to them, corneocytes retain their elasticity, thus preventing desquamation and the formation of cracks in the skin.
In the deep layers of the skin, filaggrin performs a structural function, but in the superficial layers it breaks down into osmotically active amino acids
(transurocanic acid, pyroglutamic acid and citrulline), which havehygroscopic properties
and are stable bind to water molecules.The other components of NMF are lactic acidand
urea which have hygroscopic properties; hyaluronic acid, glyceryl, lactate
, and inorganic substances such assodium, potassium, calcium and chlorine.







Add a comment