Aging of the skin of the face and neck – the result of the combined influence of natural biological processes occurring in the human body and external factors. Visible signs of aging – the first wrinkles, dullness, dryness, violation of the vascular pattern of the skin, etc. – may appear at a fairly young age.
To effectively combat the age-related syndrome, it is necessary to take into account the features of layer-by-layer aging of the face in order to choose the right anti-aging agents and methods that provide the safest and most lasting result.
Factors that lead to the appearance of signs of aging
There are 2 groups of factors, the impact of which accelerates the aging process: exogenous and endogenous. Endogenous (internal) factors include genetic characteristics, endocrine disorders, etc. The group of exogenous factors includes exposure to ultraviolet rays, bad habits, stress, etc.
Clinical and morphological features of chronoaging, predetermined at the genetic level:
- thinning of the stratum corneum and the epidermis as a whole;
- decrease in the number of epidermal cells;
- an increase in keratinocytes in size;
- change in the ratio of ceramides;
- impaired microcirculation.
Clinical and morphological features of photoaging associated with exposure to solar radiation:
- thickening and coarsening of the stratum corneum of the skin;
- dry skin;
- violation of the vascular pattern of the skin;
- massive elastosis.
Causes of the main signs of aging:
- static and dynamic wrinkles – worsening skin condition;
- folds and ptosis of tissues – relaxation of muscular-ligamentous structures;
- loss of clarity of the contours of the face and neck – gravitational ptosis and redistribution of adipose tissue.
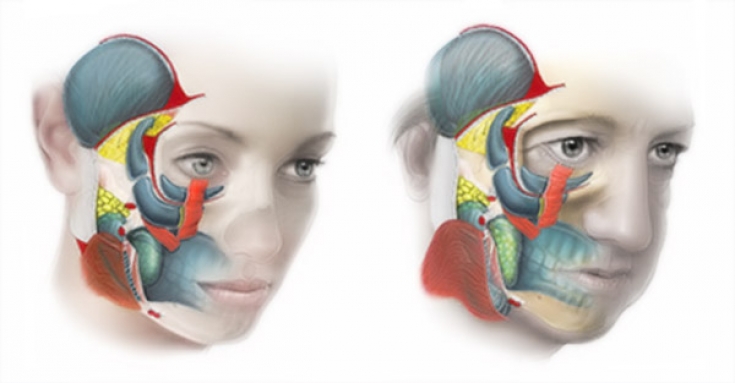
Layered aging of the face: characteristic age-related changes
-
Changes at the skin level:
- gravitational tissue ptosis;
- vector tissue movement;
- loss of elasticity, decreased tone;
- change in eyebrow position;
- drooping of the upper eyelid;
- exposure of the bony margin of the orbit of the lower eyelid;
- subzygomatic crease formation;
- formation and increase in expression of mimic wrinkles
The main cause of wrinkles – loss of firmness and elasticity of the skin. Creases and wrinkles on the face always form in a direction perpendicular to the direction of muscle contraction.
-
Age-related changes in the bones of the facial skeleton:
- reducing the height of the jaws;
- flattening of the zygomatic arch;
- thinning of the bony edge of the orbit;
- dystrophic changes in the cartilage of the nose.
To effectively solve the problem of aging, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the layered aging of the face.
-
Age-related muscle changes:
- hypertonicity of mimic muscles;
- fibrosis of muscle tissue;
- increase in adipose tissue content.
Age-related changes in muscles lead to the formation of mimic wrinkles, their transition from dynamic to static and wrinkle lengthening.
-
Age-related changes in adipose tissue:
- resorption;
- ptosis;
- atrophy and hypertrophy of adipose tissue depending on the area of the face.
With age, the original density and homogeneity of adipose tissue is lost, in older people lipoatrophy is observed – involution of adipose tissue. The main manifestations of age-related changes in adipose tissue are:
- desolation of the temporal fossa;
- nasal furrow formation;
- formation of paint bags;
- loss of zygomatic volume;
- formation of hernias of the upper and lower eyelids.
-
Age-related changes in the ligamentous apparatus:
- relaxation of the lateral canthal ligament;
- looseness of the temporomandibular joint.
Carboxytherapy from Medicare – an effective method of dealing with age-related syndrome
Skin aging manifests itself mainly at the level of two layers of this organ:
- The epidermis gradually becomes thinner due to the slowdown in cell regeneration processes. The horny (superficial) layer of the epidermis thickens, and the skin surface itself becomes dry and rough.
The dermal-epidermal junction weakens with age, as a result of which its metabolism in the skin worsens, negative changes in the microstructure of the epidermis occur.
- The thickness of the dermis also decreases with age (about 6% every 10 years). The elasticity of collagen and elastin fibers decreases, their arrangement becomes chaotic. Under the influence of enzymes, collagen fibers are destroyed, and their synthesis is reduced due to the deterioration of the function of fibroblasts. There is also a decrease in the synthesis of hyaluronic acid. Such changes lead to loss of turgor and elasticity of the skin, as well as its inability to retain moisture.
Skin lack of oxygen, accumulation of protein metabolites, exposure to free radicals, advanced glycation end products, ultraviolet radiation and other factors lead to dysfunction of skin cells.
Non-invasive carboxytherapy from Medicare, which is based on the action of molecular carbon dioxide, which is actively absorbed by the stratum corneum of the skin and increases blood oxygen saturation due to the Bohr effect.

The effect of the Medicare carboxytherapy procedure is mainly due to the fact that the cells receive enough oxygen to synthesize the energy source (ATP) necessary for the proper functioning of skin cells, their regeneration, as well as the synthesis of important components of the extracellular matrix, including collagen and elastin . In addition, cellular metabolism is enhanced, protein metabolites are excreted.
Studies have shown Medicare Non-Invasive Carboxytherapy to reduce fine lines by 56% and firm skin by 46%, and provide:
- visible lifting;
- enhance facial contours;
- improvement of skin texture and color;
- reducing the severity of acne and post-acne;
- normalization of the sebaceous glands;
- restoration of the protective function of the skin;
- free radical protection;
- excretion of protein metabolites;
- Improved lymphatic drainage.
Non-invasive MedicareCarboxytherapy can significantly improve the condition of the skin at the level of the epidermis, dermis and, accordingly, the dermal-epidermal junction. In addition, this procedure is excellent for preparing the skin for traumatic procedures (and for care after such procedures), necessary to combat other signs of layered facial aging. You can purchase drugs for non-invasive carboxytherapy, get acquainted with the protocols of procedures and get answers to all your questions by contactingMedicare.







Add a comment