In 15% of cases, couples suffer from childlessness, which means the inability to become pregnant within 12 months of sexual activity without use of contraceptive methods. In about 25% of cases, childlessness is caused by a female factor and in about 25% by a male factor.
The factor causing infertility is detected in both partners in about 25% of cases, and in the remaining 25% the cause of infertility remains unknown.
Today, doctors have extensive experience in the treatment of childlessness and unique methods of family planning, which are formed in Evidence-Based Medicine Guidelines – clinical protocols based on evidence-based medicine. Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read more about managing infertility according to the most up-to-date recommendations in our article.
Causes of childlessness according to modern treatment protocols EBM Guidelines
- The most common causes of infertility are ovulatory dysfunction (20-30%), fallopian tube problems 10-15%, endometriosis (10-20%) and sperm pathology (20-40%). Some causes of infertility become apparent only after the start of treatment.
- Decompensated medical conditions (eg, diabetes, epilepsy, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease) can reduce fertility.
- Overweight or underweight reduces, in particular, female fertility. At the same time, the risk of miscarriage increases.
- Excessive smoking impairs ovarian function and reduces the quality of sperm. Daily consumption of heavy alcohol can interfere with sperm production.
- Sperm production can be impaired due to infection, surgical pathology, testicular injury.
- Obesity reduces sperm quality.
- Sperm production may decrease with certain medications such as testosterone, cytotoxic drugs, certain antihypertensive drugs (calcium channel blockers), anabolic steroids.
Follow us on Telegram
Diagnostic program according to modern Guidelines for childlessness
1. Clinical examination is the most important examination; the appearance and structure of the patient give a lot of information about the hormonal state.
2. Blood pressure, height, weight, body hair growth and secondary sexual characteristics
3. Basic blood count with platelets, TSH, free T4, fasting blood glucose and other basic laboratory tests.
4. Pap smear and Chlamydia test during gynecological examination
5. Irregular menstrual cycle is an indication for further investigations based on other symptoms (e.g. hormonal colpocytology, measurement of prolactin, FSH, measurement of estrogen levels is not indicative).
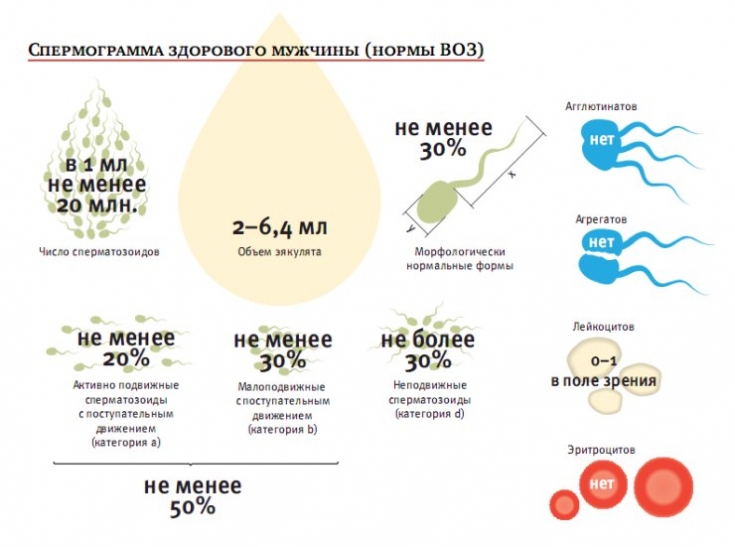
6. The first study for men - semen analysis.
7. Clinical study (read on our website: Scrotal enlargement may be a manifestation of spermatocele).
8.
9. Vaginal ultrasound provides information about the structure and function of the female reproductive organs.
10. In unclear cases, it is possible to perform hysterosonography or hysterosalpingosography, laparoscopy.
11. Gonadotropin levels are checked during the start of the cycle, if the cycle is irregular, then the concentration of anti-mullerian hormone reflects the ovarian reserve.
12. End cycle progesterone analysis is used to confirm ovulation and adequate corpus luteum activity.
13. Sperm density should be ≥ 15 million spermatozoa/ml, total spermatozoa ≥ 39 million and ejaculate volume > 1.5 ml. The sample is considered normal if the total proportion of motile sperm is ≥ 40%. During semen analysis, the content of antibodies to spermatozoa is determined.
14. Further diagnostics includes determination of the level of follicle-stimulating hormone (in case of a decrease in the amount of sperm), luteinizing hormone, testosterone, karyotype examination, Y-chromosomal microdeletions.
For more information about examination for suspected infertility, please see our article in the Gynecology section.
Treatment program according to modern Guidelines for childlessness
Clomiphene is the most commonly used ovulation induction drug according to current Guidelines. It can be used when serum prolactin and gonadotropin concentrations are normal.
- The most common cause of anovulatory infertility is polycystic ovary syndrome, PCOS. In overweight patients with PCOS, metformin can be used as an alternative treatment.
- An aromatase inhibitor is an alternative to clomiphene.
- Gonadotropin treatment is used if the patient has not responded to clomiphene or has a gonadotropin deficiency.
- Treatment is carried out using the lowest possible dose in order to mature a single ovarian follicle. Do not continue treatment after 4-6 cycles of treatment.
Ovulation induction by human chorionic gonadotropin can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. This causes abdominal pain, swelling, nausea and vomiting. May be complicated by thromboembolism, breathing difficulties or kidney failure.
- Submucosal and large (> 6 cm) intramuscular uterine fibroids should be removed.
- Tubal plasty, Salpingectomy, in case of fluid-filled and dilated tubes, may increase the chances of successful in vitro fertilization.
- Intrauterine insemination is used for semen pathology. Before insemination, semen must be separated ("washed") from seminal plasma.
- In vitro fertilization using one's own sperm or donor sperm can be used in almost all types of childlessness. Over the past few years, intracytoplasmic sperm injection has become the mainstream treatment for male infertility.
Polycystic ovary syndrome increases the risk of developing neoplasms
Measures aimed at preventing childlessness according to modern Guidelines
Reproductive health can be improved by preventing and optimally treating chlamydial infection, maintaining a normal body weight, recognizing the effect of age on fertility, and not smoking.
A woman planning a pregnancy should eat a balanced diet.
A normally healthy woman does not usually need specific dietary supplements. Vitamin B12 is recommended for women following a strict vegetarian diet. Folic acid 400 mcg/day and vitamin D 10 mcg/day are recommended by the EBM Guidelines for all women.
Infertility as a psychosocial problem in gynecology according to Guidelines
Modern treatment recommendations based on evidence-based medicine represent a wide range of interventions aimed at all possible etiological factors. But it should be remembered that childlessness is a psychosocial problem, and when faced with this, the doctor should not concentrate only on the medical aspects of the problem.
The doctor's professionalism is necessary in order to help with possible sexual problems, depression, as well as in case of a patient's feelings of guilt, anger, grief, loss.
You may also be interested in the article on our website in the "Gynecology" section: Infertility – actual problem of modern women.
According to the Evidence-Based Medicine Guidelines







Add a comment