The question of methods for closing various wounds on human skin is very relevant in modern plastic surgery. It is important to eliminate the defect in such a way that the area of the skin that has succumbed to reconstruction looks as natural as possible and retains all the functional features of a healthy area. To date, the technique of transplanting skin flaps, as well as the use of skin grafts, is widespread. Estet-portal.com shares up-to-date information about the main types of transplants used in plastic surgery today.
What types of transplants are used in modern plastic surgery
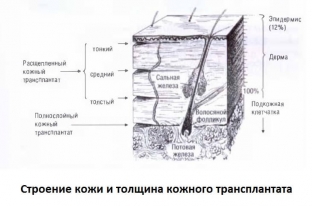
A skin graft is a section of the dermis and epidermis, which, in order to close a skin defect, is completely separated from the donor bed, does not receive nutrition from it and is not attached to it. Grafts can include different parts of sweat and sebaceous glands, capillaries and hair follicles. Depending on the origin, skin grafts are divided into xenografts, autografts and allografts. There are also such types of grafts as split and full-thickness, which depends on the components of the graft and its thickness.
Types of grafts:
- classification and features of the split type of grafts;
- types of grafts by thickness: why it is important to separate them;
- full-thickness skin grafts: characteristics and features of taking.
Classification and features of the split type of grafts
Today, the most commonly used types of grafts in plastic surgery are split-skin autografts. These grafts consist of the epidermis and part of the dermis and are classified into the following types:
- thin autografts - according to Thiersch Olli - Thiersch;
- grafts of medium thickness;
- three-quarter thick grafts.
The thickness of the graft is a very relative concept, since it is individual for each patient and depends on the age of the patient, his gender and the donor area of the body. The thickest skin is on the palms and soles of a person, and the thinnest is on the eyelids and in the area behind the ear.
Types of grafts by thickness: why it is important to separate them
It is very important for plastic surgeons to distinguish different types of grafts depending on their thickness, as this determines many important characteristics of the transplanted area:
- thin graft is subject to contraction due to the development of fibrous tissue between the recipient bed and the graft itself, thick - practically not subject to contraction;
- The survival rate of a thin graft is much higher than that of a thick graft due to better conditions for plasma absorption during the vascularization process;
- a thin graft taken from an area that has hair will not have it after transplantation, unlike a thick graft;
- after taking a thin graft, the donor surface re-epithelizes much faster than after taking a thick one.
Full-thickness skin grafts: characteristics and features of taking
Full-thickness skin graft consists of the epidermis and the full thickness of the dermis of the donor site. Such grafts after transplantation are very similar to normal skin in terms of its structure, color and hairiness. Full thickness grafts are also not subject to contraction, so they are very often chosen for defect closure. Often, these grafts are small, so the defect in the donor area is closed by mobilization and matching of the wound edges. Taking a full-thickness graft, which has a few millimeters of subcutaneous fat, is performed by transplanting after tapping the donor area with a rubber tube to small hemorrhages. Then the graft is quickly taken from the donor area and also quickly placed on the recipient bed.






Add a comment