Tuberculosis of the skin is a rather rare disease and, as a rule, has a secondary character. Tuberculosis of the skin – chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobactérium tuberculósis.
Timely diagnosis of skin tuberculosis is often associated with some difficulties, since there are atypical manifestations of the disease, there are no clear histological and morphological changes, and the response to treatment does not appear immediately.
Therefore, dermatologists need to know the classification and symptoms of skin tuberculosis in order to promptly treat pathological foci. On estet-portal.com read about the causative agent of skin tuberculosis, pathogenesis, symptoms and types of the disease.
Etiology of the causative agent of skin tuberculosis: ways of infection with mycobacteria
Mycobactérium tuberculósis belongs to a group of acid-resistant bacteria with similar properties to actinomycetes.
The microorganism has the form of a stick with rounded ends and is an aerobe or facultative anaerobe.
The skin of a healthy person is an unfavorable environment for the reproduction of mycobacteria. Mycobacteria are characterized by hematogenous and lymphogenous, contact (from neighboring organs) routes of infection, as well as autoinoculation.
Follow us on Telegram
An exogenous route of infection may occur: the pathogen enters through skin defects with the help of infected objects or from an infected person.
Pathogenesis of the inflammatory process: characteristic signs of skin tuberculosis
Most often, skin tuberculosis manifests itself as a secondary disease of tuberculosis: the patient already has primary foci in the body, usually in the lungs.
A complex combination of violations of the protective properties of the skin with reduced immunity and the development of the body's sensitivity leads to the appearance of chronic inflammatory foci.
Depending on the form of the disease, the primary element may be a hump (with lupus erythematosus), a nodule (with scrofuloderma), a papule (lichenoid tuberculosis).
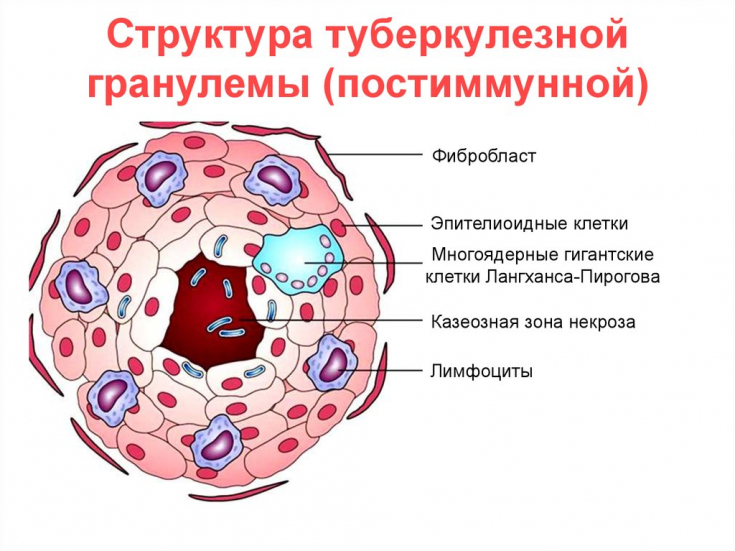
Such a pathological process is specific to Mycobactérium tuberculósis and can affect any tissue of the body.
Under what symptoms can actinomycosis be hidden?
Classification of skin tuberculosis: focal and widespread forms
Forms of tuberculosis are divided into focal and widespread variants.
In turn, the focal form is subdivided into:
• primary skin tuberculosis;
• tuberculous lupus;
• scrofuloderma;• warty tuberculosis of the skin and mucous membranes;
• miliary-ulcerative tuberculosis of the skin and mucous membranes.
The following forms are characteristic of widespread tuberculosis:
• miliary;
• papulonecrotic;
• indurative-ulcerative;
Koch's insidious wand: the bacterium that causes tuberculosis







Add a comment