Sweet – it is the most wonderful sweetener of life, everyone knows about it from birth. But since childhood, we are taught that a lot of sugar is harmful to our health. Children, for example, are afraid that candies will stick together in the bottom or the teeth will be black and not beautiful.
Today, the average person consumes about 24 kg of sugar every year. There are many scientific studies on sugar that have tried and are trying to study the positive and negative effects of this popular food substance. To be sure, the benefits of sugar are much easier to prove than the harmful effects. Now we will analyze the “why sugar” points by point: the pros of the sweet life and the cons of the “white death”.
Read on estet-portal.com
Sugar: sweetener of life or white death
Since it has become popular to organize various parades, protests, etc., soon the "sweet tooth" they will gather a rally against the radical "ppshniks" who promote the rejection of sugar.
Follow our page onInstagram!Sugar is of course responsible for many health problems, but without it your body would stop functioning properly. Naturally occurring sugars, such as those found in fruit, lactose or milk sugar, come from sources that are good for your diet. To maximize the benefits of sugar, you need to balance healthier and less healthy sources.
Immediate energy provided by sugar
Sucrose, or table sugar, is the primary source of sugar in most American diets. It is made up of one molecule of fructose and one molecule of glucose, your body's main source of energy. The body breaks down glycogen into single units of glucose for energy when primary sources are not available; between meals, at night during sleep and during exercise to prevent dangerous drops in blood sugar levels.
Read also:Top 7 Foods Causes of Depression The hormone insulin then promotes the uptake of glucose by the cells, where it is converted into energy for immediate use.

Fast assimilation by the body
The main feature of sugar – it is quickly absorbed by the human body. Sucrose, getting into our intestines, breaks down into glucose and fructose, which, when they enter the bloodstream, compensate for most of the energy losses. Glucose energy is responsible for metabolic processes. In the liver, with the help of glucose, special acids are formed – glucuronic and paired gray acids, which ensure the neutralization of toxic substances by the body.
It is for this reason that in the presence of liver diseases or in case of poisoning, sugar is taken orally or glucose is injected into the blood.
Sugar is responsible for the functioning of the brain
The functioning of the human brain depends entirely and entirely on the process of glucose metabolism. If the food we eat does not give our body a sufficient amount of carbohydrates, it is forced to receive them, using human muscle protein or proteins from other organs for their synthesis. With a lack of sugar (glucose), the tone of the central nervous system (central nervous system) significantly decreases, the concentration of attention falls, the body is less resistant to low temperatures.

Sugar: busting myths about it
Sugar does not affect the intestines and the microflora of the stomach, and does not impair metabolism at all. When used in moderation, it will not cause obesity, so it is much safer than fructose or well-publicized artificial sweeteners.
Read also:Human Gut Bacteria: Why We Get Fat and How to Lose Weight Sugar glycolic acid can be very helpful in maintaining the health and appearance of your skin. Its use can help to eliminate blemishes and restore balance in the skin's oils.
The product has a magical property of relieving the condition of irritation. When sugar enters, the pancreas produces insulin, and it stimulates the appearance of the happiness hormone – serotonin.
Sugar contains ingredients in its structure that are passed on to them from natural sources, sugar cane or beets. Elements such as phosphorus, calcium, iron, magnesium, and potassium will not be present in large amounts in refined sugar.<
The other side of the coin: the negative effects of sugar on the body
Some of this impact is immediate. Refined sugar can reduce the efficiency of white blood cells and increase markers of inflammation. In fact, obese people have fewer white blood cells with a reduced ability to fight infection.

The hormonal balance of our body
The hormonal effects of sugar and the immune system are complex, but insulin is a major player.
When you eat large amounts of sugar, your blood sugar increases. Insulin helps normalize blood sugar levels, but over time, your cells become overloaded and resistant to insulin signals.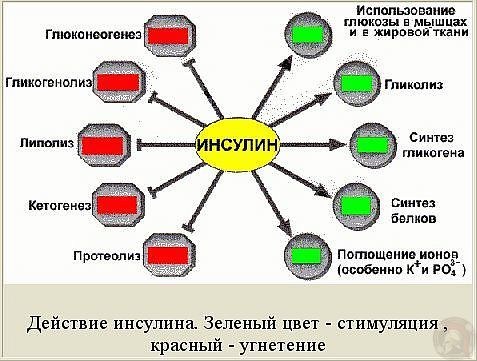
We call this condition insulin resistance, which leads to type 2 diabetes and everything related complications, including impaired immune system.
Too much sugar backfires on stress relief
But this feeling does not last long - after the initial release of dopamine, the negative effects of sugar on the brain set in.
Consumption of foods and drinks with refined sugar can cause depressive symptoms.
How sugar can weaken the immune system
Excess sugar can also affect the adrenal glands, which produce cortisol. Research shows that high amounts of sugar can keep this stress hormone constantly elevated and increase visceral fat, the most dangerous type of fat that lays the foundation for type 2 diabetes and other complications. delicious sweet food that only exacerbates psychological stress, which weakens the immune system.
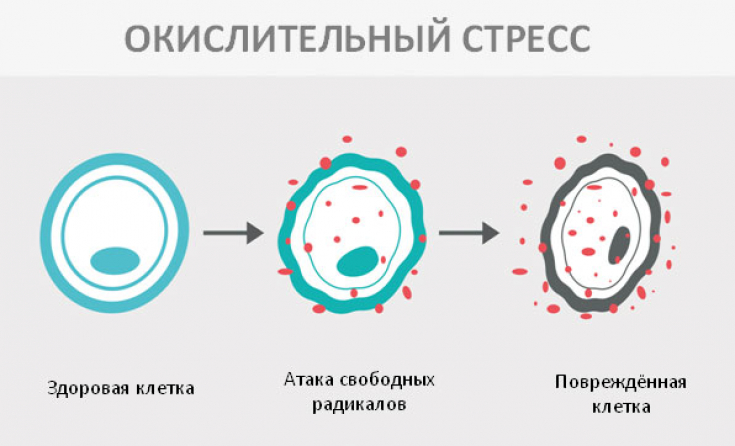
What is oxidative stress and how does sugar affect inflammation
Free radicals are a by-product of cellular metabolism. Your body's antioxidant defenses can handle normal amounts. But under certain conditions, your defense system becomes overwhelmed, leading to what is known as oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress plays an important role in virtually all chronic and degenerative diseases. Many variables can increase oxidative stress, including too much sugar.
Chronic, low-level inflammation is a key factor in many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and dementia. Sugar (especially sweetened drinks and soda) is one of those inflammation-causing factors.
Refined sugar breaks down into two simple sugars in the body: glucose and fructose. While almost every cell can use glucose, only liver cells can metabolize fructose. Studies show that fructose can increase inflammation while increasing levels of the stress hormone cortisol, which in turn increases belly fat.
Subscribe to our page on
Sugar: to be or not to be in our life
Eating too much sugar can have many negative health effects.
For these reasons, added sugar should be kept to a minimum whenever possible, which is easy if you are on a healthy whole food diet.
A sugar-free diet does not mean that you don't have to eat sugar, but avoid refined sugar in processed foods.Read also:
Dukan's Recipes: How to Diet Properly
 Fruits, legumes, sweet potatoes, and even leafy or cruciferous vegetables contain some sugar. But they also contain fiber, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and other nutrients that prevent sugar from affecting your body.
Fruits, legumes, sweet potatoes, and even leafy or cruciferous vegetables contain some sugar. But they also contain fiber, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and other nutrients that prevent sugar from affecting your body.
Watch us on YouTube:






Add a comment