The term acrodermatitis means a number of lesions of the epidermal cover, occurring with predominant localization of clinical manifestations in the lower part of the arms and legs. There are several forms of acrodermatitis, differing among themselves in terms of causes, pathogenetic changes, symptoms and methods of therapy.
Varieties of this group of skin pathologies are: enteropathic acrodermatitis, inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, idiopathic progressive atrophy of the skin caused by a bacterial infection and persistent purulent acrodermatitis Allopo (sometimes called Galoppo).
On estet-portal.com read about the diagnosis of different types of acrodermatitis and the main approaches to their treatment.
- Acrodermatitis enteropathica: features of the course of the disease
- Modern view of acrodermatitis Allopo
- Symptoms and signs of idiopathic skin atrophyand
Acrodermatitis enteropathica: features of the course of the disease
Symptoms of the disease appear soon after birth, in isolated cases enteropathic acrodermatitis – manifests at a later age.
The main reason for the development of acrodermatitis enteropathica is the absence or deficiency of the zinc-binding factor, as a result of which the concentration of this mineral in tissues, biological fluids and bones is significantly reduced.
With enteropathic acrodermatitis, the production of a number of amino acids is disrupted, cell structures change, pancreatic hyperplasia and thymus dystrophy are formed. Therefore, enteropathic acrodermatitis is accompanied not only by symptoms from the epidermal cover, but also by disturbance of the functioning of internal organs. With untimely diagnosis and lack of treatment, the disease is fraught with death.
Skin manifestations may coincide in time with those of the digestive tract or appear earlier or later.
Initially, pustular eruptions localize on the hands and feet, then spread above – on large joints of the limbs, cover the perineum, genitals.
How to recognize microbial eczema
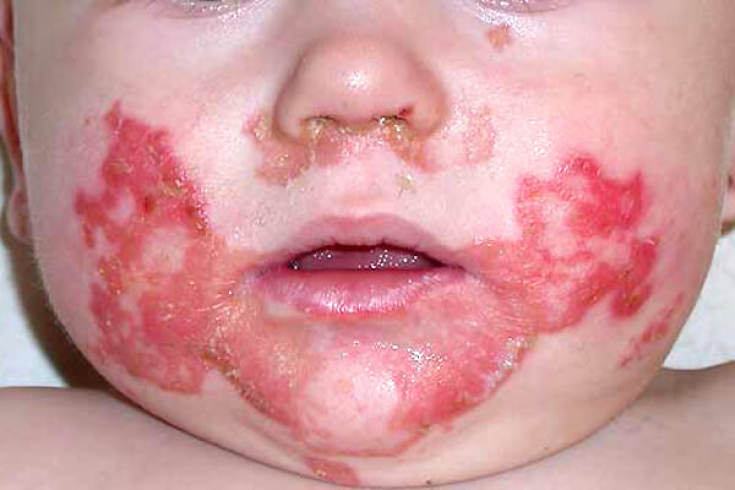
In acrodermatitis enteropathica, the rash is characterized by confluence into extensive foci with a symmetrical arrangement. In a number of patients, the appearance of the lesions is similar to the symptoms of psoriasis, eczema, fungal dermatosis. Also note the violation of the growth of hair on the head, eyebrows and eyelashes. Acrodermatitis occurs with pronounced digestive disorders:
- appetite worsens;
- flatulence and persistent diarrhea appear;
- feces have a slimy consistency and a sharp putrid odor, contain undigested food residues.
Further progression of enteropathic acrodermatitis affects the general well-being of the patient. fever sets in, child growth stops, weight gain stops. Doctors pay attention to weakness, drowsiness, apathy. Differential diagnosis is carried out with other hereditary congenital dermatoses, eczema and psoriasis. The basis of therapy is zinc preparations, and the dosage is calculated depending on the severity of the symptoms. The treatment is long-term, after the condition improves, the patient is transferred to maintenance doses of medications.
Lack of therapy for enteropathic acrodermatitis leads to the progression of the pathology, a secondary bacterial or fungal infection joins the skin and digestive symptoms. High chance of death.
When a Dermatologist Saves a Life: Skin Infections in the ICUii
Modern view of acrodermatitis Allopo
The etiology of Allopo's acrodermatitis is unknown, sometimes the disease is associated with an infection or trauma. Acrodermatitis Allopo proceeds with damage to the extreme phalanges of the fingers, less often – legs. Pathology manifests with the appearance of pustular or scaly rashes, abscesses on the thumb. Then the process spreads to other phalanges.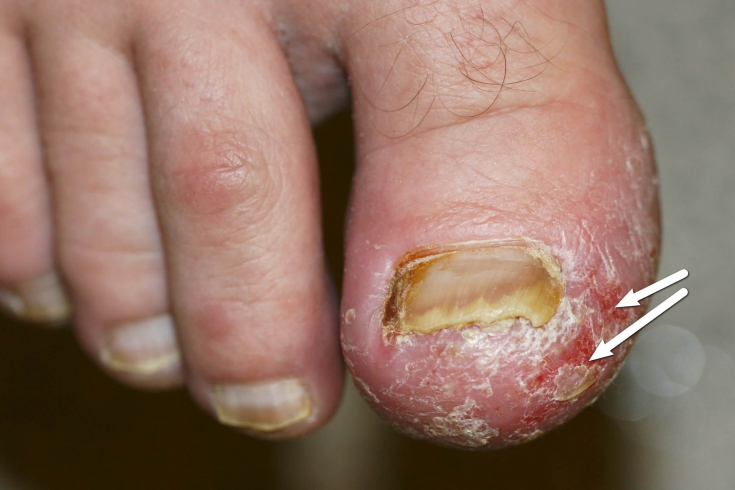
With Allopo's acrodermatitis, a change in the shape of the terminal phalanges occurs, dystrophy of the nail plate is noted up to complete rejection. To eliminate the signs of acrodermatitis, Allopo is prescribed steroid drugs, physiotherapy, local baths with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory solutions.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Symptoms and signs of idiopathic skin atrophy
This form of acrodermatitis has an infectious etiology. The causative agent of the disease are spirochetes of the genus Borrelia, penetrating the epidermis with a tick bite. The onset of the pathology is not acute, with rashes on the lower extremities, spreading throughout the body, including the face.
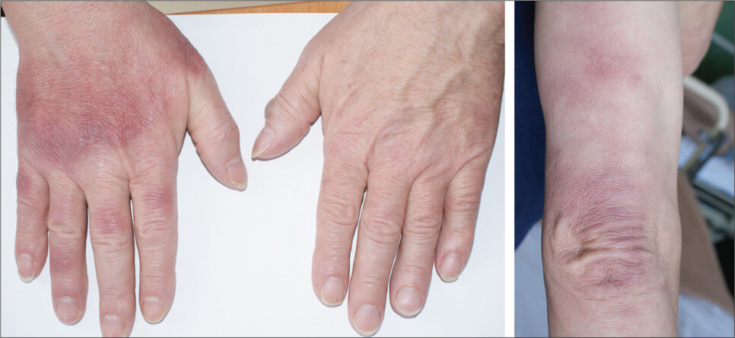
After the inflammatory process subsides, acrodermatitis causes atrophic changes in the epidermis with impaired sweating and pigmentation.
With idiopathic atrophy of the skin, the risk of complications is high, up to the appearance of malignant processes. For the treatment of acrodermatitis, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity are prescribed.
Causes of toxic skin reactions







Add a comment