Atopic dermatitis refers to a type of allergy, from "derma, dermatos" − skin, and «it» − inflammation.
Thus, atopic dermatitis describes inflammation of the skin that is the result of an allergy.
This dermatitis occurs as a result of the reaction of the immune system after skin contact with an irritant (allergen), leading to dry rashes accompanied by itching, especially on the folds of the body − in areas such as the crook of the wrist, the inside of the elbows, the back of the knees, and exposed skin such as the face, palms and feet.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what role does the immune system play in the mechanism of occurrence atopic dermatitis.
- The first phase of atopic dermatitis
- The second phase of the development of atopic dermatitis as a manifestation of an allergic reaction
- Atopic dermatitis symptoms in different age groups
- Approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitisa
The first phase of atopic dermatitis
When the immune system begins to attack its own body− it is a hypersensitivity reaction. There are four types of it.
Atopic dermatitis − it is a hypersensitivity reaction type one that starts with an external allergen trigger such as pollen or dust mites.
Follow us on Instagram!
Pollen can penetrate the pores of the skin, where it is met by immune cells in the next layer of tissue.
Immune cells are called antigen presenting cells because they present the allergen particle to intact T-leukocytes, converting them into Th2 cells.
Then, these cells Th2 - lymphocytes activate the surrounding B-lymphocytes, which are ready to start producing immunoglobulin E, i.e. antibodies specific to that allergen.
These antibodies attach to the surface of other immune cells called mastocytes as well as to basophils that reside in tissues just under the skin.
This process is called sensitization.
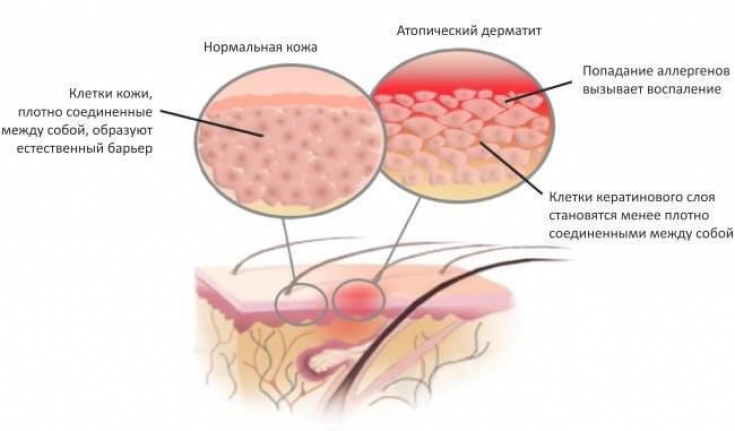
The second phase of the development of atopic dermatitis as a manifestation of an allergic reaction
Now imagine that the pollen is re-penetrated through the skin.
In this case, the allergen can bind to immunoglobulin E on sensitized cells, resulting in degranulation or the release of large amounts of pro-inflammatory molecules such as histamine, leukotrienes >and protease.
Management of atopic dermatitis: updated recommendations
The combined effect of these molecules causes the surrounding vessel walls to become permeable to fluid, which attracts even more immune cells to the site and causes skin inflammation in the area.
This inflammatory reaction makes the skin barrier more "permeable" and can be "overpassed" by more allergens, at the same time, more moisture is lost because of this, the skin becomes dry and cracked.
Dry skin causes itching. When a person combs it, it damages even more, intensifying the process.
A vicious circle of allergic inflammation, dry skin and itching is formed that characterizes atopic dermatitis.
Sometimes, bacteria enter the body through damaged skin, increasing inflammation.Atopic dermatitis usually begins in early childhood, but also often continues or recurs
in adults, usually with a hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children of different age groupsIn infants, the rash most often occurs on the face and scalp, and in older children − on bending surfaces.
The course of atopic dermatitis may be aggravated by:
- additional allergens (cigarette smoke, mold);
- changes in weather conditions;
- emotional stress.
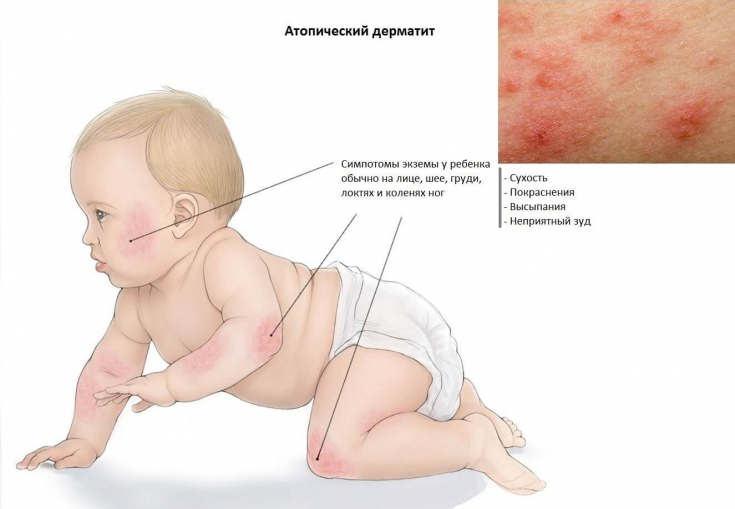
The skin may become scabbed after a while.
Most often
itching bothers at night, and perhaps because children are not distracted, they mechanically damage eczema areas.
Genetics plays a decisive role in the development of atopic dermatitis.
People with atopic dermatitis often also have asthma and atopic rhinitis. Collectively, this is called theatopic triad.
These diseases often have a hereditary component and may occur in close relatives.
What a dermatologist should know about hives in children
Sometimes atopic dermatitis can be part of a syndrome, such asHyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome, which has an autosomal dominant form − Job's syndrome.
Alternative −Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome − An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by the clinical triad of eczema, thrombocytopenia, and immunodeficiencym.
Therapeutic efficacy of histamine blockers in eczema
Approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitisAtopic dermatitis is generally a clinical diagnosis.
There are ways to help break the cycle of allergic inflammation.
Therapy for atopic dermatitis includes:
- denial of access to allergens;
- skin hydration;
- minimization of itching,
- suppression of allergic reactions in severe cases.
avoid any triggers, including overheating, stress, and dress in soft fabrics that do not irritate the skin.
Dry skin can be helped by moisturizing frequently, best done after a warm shower.Itching can be controlled by cutting your nails short and trying to keep children from scratching.
But for more serious cases, there are also
steroids and calcineurin inhibitors − they suppress the immune response.
Antihistamines, antibiotics can also help with itching if there is skin contamination with a pathogen.






