Lichen planus is a peculiar reaction of the organism of unidentified etiology, which manifests itself as a monomorphic papular rash on the skin and mucous membranes. This skin disease is considered to be multifactorial. External and internal factors, along with genetic abnormalities, can play a significant role in the formation and course of the pathological process in lichen planus.
Today, lichen planus is considered as a chronic dermatosis, characterized by the appearance on the skin, oral mucosa or on the external genital organs of monomorphic flat papules with a waxy sheen. Learn more about lichen planus at estet-portal.com.
Causes and forms of lichen planus
The cause of lichen planus cannot be considered definitively established. In the development of dermatosis, a large role is played by infectious factors (viruses), toxic-allergic effects, as well as neurogenic and immune disorders.
Researchers who speak out for the infectious nature of dermatosis refer to the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy, cases of family disease, and the detection of intracellular viral inclusions in these patients.
& nbsp; Lichen planus of the skin and mucous membranes is distinguished by a wide variety of atypical forms, which greatly complicates diagnosis, notes estet-portal.com. It is customary to distinguish six forms of lichen planus on the mucous membrane of the mouth and the red border of the lips.
The main forms of lichen planus:
- typical;
- exudative-hyperemic;
- erosive-ulcerative;
- bullous;
- hyperkeratotic;
- atrophic.
Clinical manifestations of lichen planus
The most common form of lichen planus is characterized by a monomorphic rash formed by lenticular, inflammatory, shiny, polygonal papules, on the surface of which one can see Wickham's mesh pathognomonic for the disease in the form of opal-like white or grayish dots and stripes. In order for the mesh to really become noticeable, it is necessary to moisten the surface of the papules & nbsp; vaseline or vegetable oil, or water.
In most cases of lichen planus, along with the skin, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity & nbsp; and external genital organs are also affected, lesions can be isolated or combined with skin lesions.
First, small grayish-white papules appear, clearly visible against the pink background of the mucosa, then plaques form. More often they are localized on the inner surface of the cheeks along the line of contact of teeth (molars), where they form a whitish pattern, similar to a fern leaf.
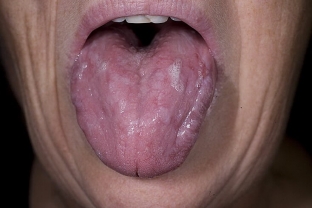
Aspects of treatment of lichen planus
Therapeutic management of patients with lichen planus is always complex. Currently, due to the lack of a unified concept regarding the etiology and pathogenesis of lichen planus, there are numerous methods of therapy for this disease.
Paying full attention to the complexity of the pathogenesis of lichen planus, success in the treatment of patients can only be achieved if treatment is started in a complex and individual way, using modern techniques.
Traditional treatment consists of antibiotic therapy, sedatives and antihistamines, topical glucocorticosteroids, vitamins (A, D, E), retinoids (vitamin A derivatives), enterosorbents, immunomodulators, exogenous interferonogens.
The action of retinoids is aimed at removing the inflammatory response and improving skin proliferation.
Complex treatment of lichen planus is also carried out using topical glucocorticosteroids of strong and very strong action.







Add a comment